Trigger Asynchronous AWS Automations via Lambda Cloudformation Triggers

Summary
An AWS CloudFormation Custom Resource can be complicated to setup: It requires a provided Service Token, an AWS service that can handle a requests from the Service Token, and then return a response to the Custom Resource. This can be very time consuming to create, especially when the intended use case is to simply run an AWS Lambda function during deployment. This pattern provides drop in code to successfully trigger any lambda function during an AWS CloudFormation stack deployment.
A Custom Resource can be useful when creating or configuring an AWS resource that is not configurable from CloudFormation. There are various AWS services that were historically not fully supported by CloudFormation or had limitations such as AWS Resource Groups and Tag Editor, AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall), AWS Certificate Manager Private Certificate Authority, etc. Using the CloudFormation Custom Resource is an easy way deploy Cloudformation nonconfigurable resources via a Lambda function.
All example code for this can be found in my Github repository.
Disclaimer: This pattern is for triggering a Lambda function, which means the CloudFormation Custom Resource will NOT wait for the triggered Lambda function, in our case “helloWorld”, to complete. This pattern is to be used when the success of the triggered Lambda function is not integral for the CloudFormation Custom Resource success, or for subsequent CloudFormation steps.
If you want the Custom Resource to wait for successful completion of a Lambda function, you only need the customLambdaInvokerTriggerLambda function with cfnresponse.send() appended at the end to send a success/failure response back to the Custom Resource. This pattern is still useful in showing how to zip dependencies for a Lambda function ran as part of a CloudFormation Custom Resource.
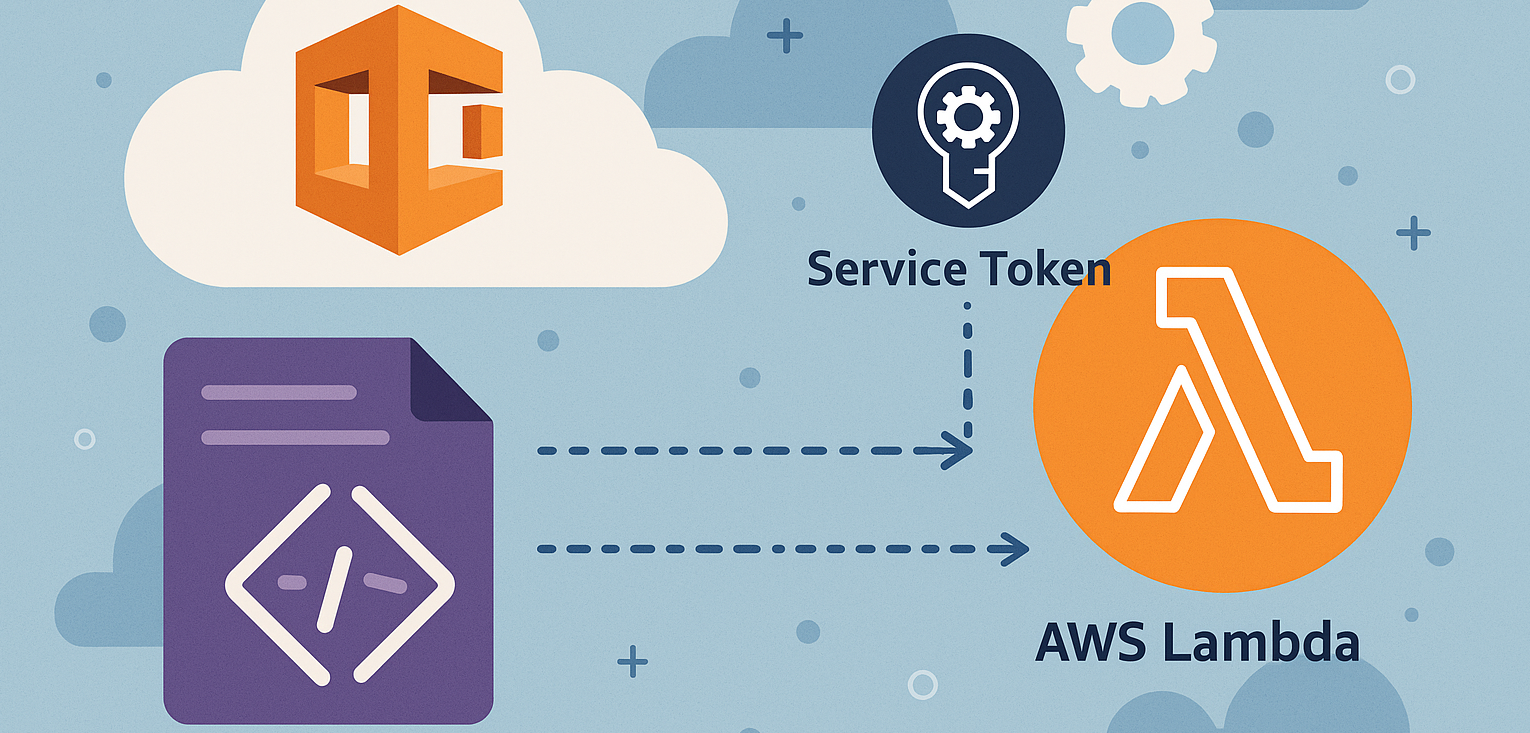
Architecture
Target Technology Stack
Target Architecture

There are two CloudFormation YAML files used to deploy this pattern. The first, lambdaCodeS3BucketCreate.yaml, creates an S3 bucket to house the lmabda code. The second, cfnLambdaTrigger.yaml deploys the Custom Resource and the a helloWorld lambda funtion that represents creating or configuring CloudFormation configurable resource.
lambdaCodeS3BucketCreate.yaml
A. An S3 bucket called cloudformation-lambda-trigger is created to store the zipped Lambda functions customLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger.py and helloWorld.py. After the S3 bucket is created, a user needs to upload the zip files. This can be done automatically using the CLIDeploy.sh script via a bash terminal. This can also be done via the console by first running the ConsoleDeploy.sh script, then copying the zipped functions in the /lambda/zips folder to the cloudformation-lambda-trigger S3 bucket.
B. The zipped Lambda function customLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger.py + dependencies
C. The zipped lambda function helloWorld.py
cfnLambdaTrigger.yaml
D. An AWS CloudFormation Custom Resource called CustomLambdaInvokerCustomResource runs and uses the CustomLambdaInvokerTrigger’s Amazon Resource Name (ARN) as a Service Token.
E. The AWS Lambda function customLambdaInvokerTrigger is invoked. This AWS Lambda uses the AWS cfnresponse module. The AWS Lambda function asynchronously invokes the wanted function, in our case the helloWorld function. The function CustomLambdaInvokerTrigger then sends a special cfnresponse.SUCCESS response back to the Custom Resource CustomLambdaInvokerCustomResource. This unique response is required for the stack to consider the Custom Resource deployment successful and continue or complete the stack deployment.
F. The AWS Lambda function helloWorld is invoked and prints the Events and Context to Logs. This is where you specify actions/services to deploy.
Deploy via the AWS CLI [Recommended]
Navigate to root folder of the locally downloaded repository files and run the CLIDeploy.sh file in a bash terminal with the command bash CLIDeploy.sh . If you do not have a bash terminal available, open up the CLIDeploy.sh file and recreate the same steps by hand or in another language supported by your terminal. Make sure that your terminal properly connects to AWS CLI and also has python installed and can run python3 commands. There are plenty of guides online to help you set that up.
And that is it! If you encounter any errors, they will be printed in the terminal.
Below is a brief description of what the CLIDeploy.sh script does:
- Uses
pipto install required package files. - Creates a virtual environment.
- Zips the package files and Lambda function
customLambdaInvokerTriggertogether and places it in the/lambda/zipsfolder - Zips any other python files in the
/lambdafolder that don’t require dependencies and places it in the/lambda/zipsfolder - Creates the S3 bucket
cloudformation-lambda-triggervia deploying the stacklambdaCodeS3BucketCreate.yaml - Uploads the zip files in
/lambda/zipsto the S3 bucket - Creates the CloudFormation Custom Resource and triggers the Lambda function
helloWorldvia deploying the stackcfnLambdaTrigger.yaml
Deploy via the AWS Console
-
Navigate to the AWS Console, then to the CloudFormation page. Click on
Create stack, then Create with new resources (standard). Give the stack a name, and deploy. This will create an S3 bucket calledcloudformation-lambda-triggeris created to store the zipped Lambda functionscustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger.pyandhelloWorld.py. -
After the S3 bucket is created, the zipped Lambda functions need to be uploaded to the
cloudformation-lambda-triggerbucket. To do this, navigate to root folder of the locally downloaded repository files and run theConsoleDeploy.shfile in a bash terminal with the commandbash ConsoleDeploy.sh. If you do not have a bash terminal available, open up theConsoleDeploy.shfile and recreate the same steps by hand, which include usingpipto install required package files, creating a virtual environment, then zipping the package files and Lambda function together. If it successfully ran, you should see no errors in the terminal command line as well as two zipped Lambda files calledcustomLambdaInvokerTrigger.zipandhelloWorld.zipin the/lambda/zipsdirectory. -
Navigate to the S3 bucket that starts with
cloudformation-lambda-trigger. You will see that it has a random alphanumeric string at the end. This is to keep the S3 bucket consistently unique. Upload the two zipped Lambda files calledcustomLambdaInvokerTrigger.zipandhelloWorld.zipto the root of the bucket. -
Navigate to the AWS Console, then to the CloudFormation page. Click on
Create stack, thenCreate with new resources (standard). Give the stack a name, and deploy. This will create the CloudFormation Custom Resource that will eventually trigger thehelloWorldLambda function to create or configure a CloudFormation non configurable resource. You can verify that this pattern deployed properly if the stack has the statusCREATE_COMPLETE.
How to create your own CloudFormation Custom Resource
Create an AWS CloudFormation Custom Resource
Add a Custom Resource Block to an Existing AWS CloudFormation Stack
Add the following AWS CoudFormation Custom Resource block to your YAML file:
CustomLambdaInvokerCustomResource:
Type: AWS::CloudFormation::CustomResource
DependsOn: CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger
Version: "1.0"
Properties:
ServiceToken: !GetAtt CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger.Arn
You can find this Custom Resource block inside of the cinfLambdaTrigger.yaml template.
Notice there is a DependsOn for the Lambda Invoker Lambda function CustomLambdaInvokerTrigger.Arn. What this means is that the Lambda Trigger, and the wanted Lambda run before the Custom Resource is created. You might wonder then why we even need the Custom Resource.
If we had created the wanted Lambda function itself, there would not be a trigger event attached to the Lambda function, meaning it would never run.
If we had created the wanted Lambda and the CustomLambdaInvokerTrigger Lambda functions, we could trigger the wanted Lambda function, but then the stack would not be aware if the wanted Lambda ran successfully.
Creating the Custom Resource guarantees a status response will be sent back to the stack during deployment.
Specify the attached Service Token
CustomLambdaInvokerCustomResource:
Type: AWS::CloudFormation::CustomResource
DependsOn: CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger
Version: "1.0"
Properties:
ServiceToken: !GetAtt CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger.Arn
Notice there is a ServiceToken Property on the Custom Resource. The Service Token specifies where AWS CloudFormation sends a request to: in this case the CustomLambdaInvokerTrigger Lambda function.
Create the Lambda Invoker Lambda Function
Create the Lambda Invoker Lambda IAM Role
The Lambda Invoker Lambda function requires an IAM Role. A Lambda execution role is required by all Lambda functions to give the Lambda function the ability to interact with other AWS Services and Objects. Here is the IAM Role used for the CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger Lambda function:
CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTriggerRole:
Type: "AWS::IAM::Role"
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: "Allow"
Principal:
Service:
- "lambda.amazonaws.com"
Action:
- "sts:AssumeRole"
Path: "/"
Policies:
- PolicyName: "InvokeLambdaPolicy"
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: "Allow"
Action: "lambda:InvokeFunction"
Resource: !GetAtt LambdaHelloWorld.Arn
You can find this Custom Resource block inside of the cinfLambdaTrigger.yaml template.
This role permits CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger Lambda function to invoke the LambdaHelloWorldLambda Lambda function. Make sure to change the Resource: !GetAtt LambdaHelloWorldLambda.Arn to the ARN of your wanted lambda. Everything else in the Role should stay the same.
This role permits CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger Lambda function to invoke the LambdaHelloWorldLambda Lambda function. Make sure to change the Resource: !GetAtt LambdaHelloWorldLambda.Arn to the ARN of your wanted lambda. Everything else in the Role should stay the same.
Create the Lambda Invoker Lambda Resource
import boto3
import json
import cfnresponse
from botocore.response import StreamingBody # Import the StreamingBody class
lambda_client = boto3.client('lambda')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
try:
if event['RequestType'] == "Create":
cfn_event = {} # Ability to pass parameters
# Invoke Lambda function and capture the response
invoke_response = lambda_client.invoke(
FunctionName='LambdaHelloWorld',
InvocationType='Event', # RequestResponse for synchronous invocation and Event for asychronous invocation
Payload=json.dumps(cfn_event)
)
# Check if the invocation was successful: 200 for synchonous and 202 for asynchronous (meaning event queued)
if invoke_response['StatusCode'] == 200 or invoke_response['StatusCode'] == 202:
# Convert the dictionary to a new dictionary where the StreamingBody content is converted to a string
serializable_dict = {}
for key, value in invoke_response.items():
if isinstance(value, StreamingBody):
# If the value is a StreamingBody, read its content and convert to a string
content_str = value.read().decode('utf-8')
serializable_dict[key] = content_str
else:
# If not a StreamingBody, include as is
serializable_dict[key] = value
# Convert the new dictionary to a JSON-formatted string
responseValue = json.dumps(serializable_dict)
else:
responseValue = f"Lambda invocation failed with status code: {invoke_response['StatusCode']}"
responseData = {'InvokedLambdaResponse': responseValue}
cfnresponse.send(event, context, cfnresponse.SUCCESS, responseData, 'LambdaHelloWorld-customresource-id')
This Lambda function is responsible for invoking the wanted Lambda function helloWorld and returning a special cfnresponse.SUCCESS response back to the Custom Resource CustomLambdaInvokerCustomResource.
You can find this code block inside of the /lambda/customLambdaInvokerTrigger.py file.
Function item to modify for your function:
lambda_client.invoke(FunctionName=’’) - Make sure to change the function name to the name of the wanted Lambda so that the correct Lambda function is invoked.
In the cfnLambdaTrigger.yaml stack we can see the above Lambda function is deployed using the following resource:
CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
DependsOn: LambdaHelloWorld
Properties:
FunctionName: "CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTrigger"
Role: !GetAtt CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTriggerRole.Arn
Runtime: python3.11
Handler: customLambdaInvokerTrigger.lambda_handler
Timeout: 30
ReservedConcurrentExecutions: 1
Code:
S3Bucket: !ImportValue LambdaCodeS3BucketName
S3Key: "customLambdaInvokerTrigger.zip"
CloudFormation item to modify for your function: DependsOn - Change the DependsOn resource to the last resource you want to deploy before triggering the wanted Lambda function. Here we have set it to the LambdaHelloWorld resource to ensure the function is created before attempting to trigger it.
Return to the code block inside of the /lambda/customLambdaInvokerTrigger.py file to continue.
(Optional) Add Parameters to Send to Wanted Lambda
cfn_event = {} # Ability to pass parameters
If there are parameters than need to be sent to your wanted Lambda, you can include them in JSON format to the cfn_event dictionary. The cfn_event dictionary is passed to the wanted Lambda function as the event parameter at runtime.
(Optional) Modify the CFN Response ID
cfnresponse.send(event, context, cfnresponse.SUCCESS,
responseData, 'LambdaHelloWorld-customresource-id')
The LambdaHelloWorldLambda-customresource-id string in the cfnresponse.send() represents the physicalResourceId.
The physicalResourceId is a unique identifier of the custom resource that invoked the function. By default, the module uses the name of the Amazon CloudWatch Logs log stream that's associated with the Lambda function.
The value returned for a physicalResourceId can change custom resource update operations. If the value returned is the same, it's considered a normal update. If the value returned is different, AWS CloudFormation recognizes the update as a replacement and sends a delete request to the old resource.
Deploy the AWS CloudFormation Stack and Verfiy Success
See the Deploy sections above.
Additional Information
Prerequisites and limitations
Access to an AWS Account
An AWS account is needed to deploy this stack. The AWS account used will also need permission to deploy AWS CloudFormation stacks and AWS Lambda.
Install AWS CLI (Optional but Recommended)
To deploy this CloudFormation stack via command line, you will need to install the AWS CLI. Installation instructions vary per operating system, so check out the latest documentation here to install for your specific operating system. Remember to ensure that your associated AWS CLI account has the necessary permissions to deploy and describe CloudFormation stacks.
Install Python
To install Python version 3 on most operating systems, you can download the appropriate installer for your operating system from the official Python website at python.org.
The latest version currently is Python 3.11. If there is an updated version in the future, it should be compatible. Alternatively, some operating systems such as Linux provide a package manager that can be run to install Python.
On macOS, the best way to install Python involves installing a package manager called Homebrew.
Once you have downloaded and run the installer you can verify that Python is installed by opening a command prompt and typing python --version.
Python is required to download the dependencies required by the Lambda function customLambdaInvokerTrigger.py.
Tools
AWS Services
-
AWS CloudFormation is a service that allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure as code (IaC). Instead of manually creating and configuring AWS resources, you can use CloudFormation templates to declare the resources you need and their configurations. An AWS CloudFormation stack is deployed to show functionality of a CloudFormation Custom Resource Lamnda trigger.
-
AWS Lambda is a compute service that helps you run code without needing to provision or manage servers. It runs your code only when needed and scales automatically, so you pay only for the compute time that you use. AWS Lambda is used to invoke another AWS Lambda function that logs the Event and Context and returns a SUCCESS response to the AWS CloudFormation Custom Resource.
-
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) specifies who or what can access services and resources in AWS, centrally manages fine-grained permissions, and analyzes access to refine permissions across AWS. An AWS IAM CustomLambdaInvokerLambdaTriggerRole Role is used to give the AWS Lambda function CustomLambdaInvokerTrigger permission to invoke the wanted function LambdaHelloWorldLambda.
Python
- Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Python is used in this pattern for both the
customLambdaInvokerTriggerandhelloWorldAWS Lambda functions.
Best Practices
Least Privilege IAM Policies
IAM best practices involve using the principle of least privilege, which means granting users only the permissions they need to perform their tasks. By strictly controlling access, you reduce the chances of accidental or intentional misuse. These principles are applied to the IAM Role policies used in this pattern.
Building Serverless Services
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It is an excellent choice for web scraping because it is highly scalable, easy to use, and has a low cost. You pay only for the compute time you consume - there is no charge when your code is not running. The use of AWS Lambda functions in this pattern provide the most time and cost effective way to deploy resources via Lambda and also return a SUCCESS to the AWS CloudFormation stack.